COMMUNICATION:
Communication is the process of converting (or) transferring of information
from one point to another point..Information can be image, text (or) any other
data. Communication between any two points (or) place requires a medium in
between them. This medium can be wired (or) wireless medium.
TYPES OF COMMUNICATION:
Communication can
be two types:
1. Analog communication
2. Digital communication
1. Analog communication: Analog communication the transmit
information is continuous in nature.
2. Digital communication: Digital communication the transmit
information is discrete in nature.
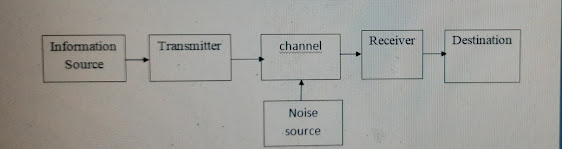
Basic block diagram for communication system
Information Source:
·
The objective of any communication
system is to convert information from one point to the other .The information
comes from the information source.
·
The information source converts this
information into physical quantity.
· The
physical manifestation of the information is termed as message signal.
Transmitter:
·
The objective of the transmitter block
is to collect the incoming message
signal.
·
Channel is a physical medium which
connects the transmitter block with the receiver block.
· The functionality of the transmitter block is mainly decided by the type of the channel chosen for communication.
· Channel is the physical medium which connects the transmitter with that of the receiver.
·
The physical medium includes copper
wire, coaxial cable, fiber optic cable, wave guide and free space or
atmosphere.
·
The choice of a particular channel
depends on the feasibility and also the purpose of the communication system.
Receiver:
·
The receiver block receives the incoming
modified version of the message signal from the channel and processes it to
recreate the original from of the message signal.
·
There are a great variety of receives in
communication systems ,depending on the processing required to recreate the
original message signal and also final presentation of the message to the
destination.
Destination:
· The destination is the final block in the communication system which receives the message signal and process it to comprehend the information present in it.
MODULATION:
The
process of changing any one of the characteristics of carrier signal with
respect to information signal is known as modulation.
Modulation is classified into two types:
1.Analog modulation
2.Digital modulation
1. Analog
modulation: In analog modulation both information and carrier
signal in nature.
2. Digital modulation:
In digital modulation information signal is digital and carrier signal is
analog in nature.
AMPLITUDE MODULATION:
It is the process of changing the amplitude
high frequency carrier signal in accordance with low frequency information
signal. Here frequency and phase angel of carrier remains unchanged.
FREQUENCY
MODULATION :
It is the process of changing the frequency of carrier signal accordance with amplitude of information signal.
PHASE MODULATION
:
It is the process of changing the phase of
carrier signal accordance with amplitude
of information signal.
AMPLITUDE
SHIFT KEYING (ASK):
·
Amplitude
shift keying is a form of amplitude modulation that represents digital data as
variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave.
·
Amplitude
shift keying uses a finite number of amplitudes , each assigned a unique
pattern of binary digits.
FREQUENCY SHIFT KEYING (FSK):
·
FSK is the digital modulation technique
in which the frequency of carrier signal varies according to the digital signal
changes FSK is a scheme of frequency modulation.
PHASE SHIFT KEYING (PSK):
·
Phase shift keying is a digital
modulation process which conveys data by changing the phase of a constant frequency reference
signal.
·
PSK uses a finite number of phases each
assigned a unique pattern of binary digits.






0 Comments